Who knows your cat better than you? Nobody! However, cats hide almost everything (especially pain), so you might not realize that they’re hurting. Their cryptic behavior is a hold-over from their past, when they lived in the wild instead of our living rooms. Back then, cats who showed signs of illness and pain stood out to predators, and masking their discomfort was a key survival strategy. In the safety of our living rooms, cats are more comfortable and therefore may be likely to show signs of their pain.
When cats are in unfamiliar places (like a veterinarian’s exam room), it’s doubtful they’ll show signs of joint pain. Plus, normal cat behavior varies from cat to cat. That’s why your veterinarian relies on you to report changes in your cat’s behavior for more accurate diagnoses. Exactly how well you know your cat — their personality, daily habits, and silly quirks — is critical when it comes to their health. This way you can more easily tell when something isn’t right.
Establishing Your Cat’s Normal (or at Least a Baseline of Their Behavior Today)
Getting to know and documenting your cat’s normal behaviors establishes a baseline, much like what your veterinarian does during annual wellness visits. They want a reference point for bloodwork, urine, weight, and other health factors to know what’s normal for your cat. Detecting a change is much easier with a baseline — even small changes in cat behavior potentially big problem.
If you’ve known your cat since they were a kitten, establishing a baseline of what’s normal can start as early as you’d like (but start when cat is at least a year old and now an adult). Taking short videos of your cat doing normal activities is a great way to track their behaviors over time.
It’s a little trickier if you’ve rescued or adopted your cat. In this situation, the original baseline you established might change as you and your veterinarian identify conditions for treatment, and you start to see positive changes from the baseline. In either case, your observations of how your cat behaves at home are critical data points to measuring your cat’s health and well-being.
Getting Started: What’s Normal for Your Cat?
Cats have common behaviors and capabilities. To what degree, frequency, or duration that they exhibit these are what make their normal cat behavior unique. To establish a baseline for your cat’s behaviors and habits, consider the following:
- Climbing up or Down Stairs*
Does your cat typically move in one fluid motion from top to bottom, take their time and carefully place their feet on each step, reflect along the way, or hesitate and move with effort, possibly stopping in a crouched position? - Jumping up to or Down From the Counter*
Does your cat frequently jump up to the counter in one single leap? Does your cat like to take smaller, part-way jumps, maybe pulling themselves up or reaching down first? - Hunting or Playing*
Does your cat engage in this activity every time you play or just occasionally? Does your cat keep up with the object or lag behind? - Running*
Does your cat tend to run in bursts of energy or more when they’re startled? Does your cat run in a fast, fluid motion, or do they move more slowly, perhaps alternating between a jog and a walk? - Socializing
Is your cat a social butterfly, more reserved, or do they prefer “alone time”? How do they act around visitors? How much time does your cat spend interacting with you and other family members (human or pet)? - Grooming
How much time does your cat spend grooming themselves? Are they able to bend in all kinds of directions or do they have difficulty with reaching certain spots? Are they looking scruffy? - Vocalizing
How talkative is your cat? Do they talk a lot or are they usually quiet? - Eating
Does your cat have a big appetite, or do they tend to be more finicky? - Sleeping
Where does your cat typically like to sleep and how often do they sleep? - Using the Litter Box
How frequently does your cat use the litter box? Does your cat miss the litter box?
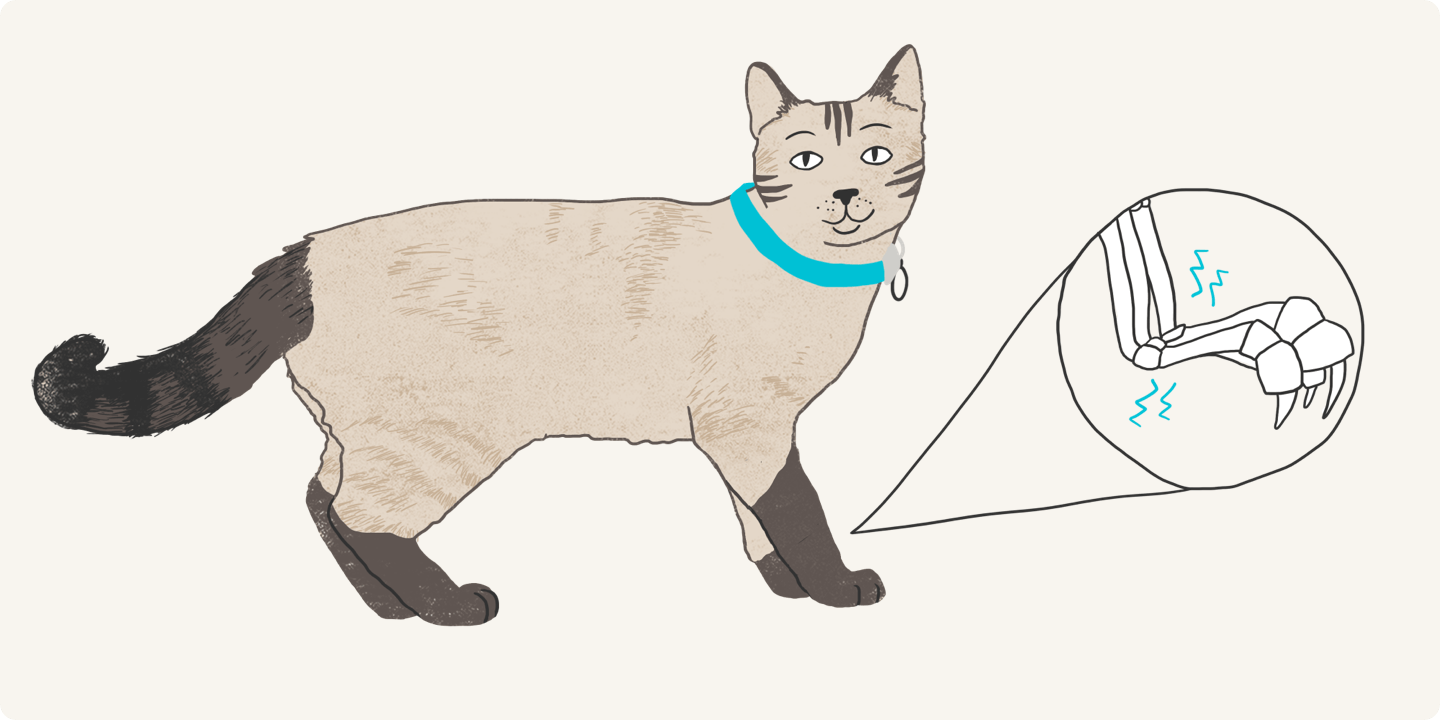
Having a good grasp on what’s normal for your cat means you’ll know when they aren’t feeling well. For example, negative changes in the first four of these behaviors (marked with an asterisk*) have been correlated with a clinical signs of cat osteoarthritis (OA), a progressively painful disease that leads to changes in energy, behaviors, vital signs, and even personality1. Fortunately, there's pain management for your cat if they are diagnosed with OA
Check out this cat OA quiz to see animations illustrating healthy cats and OA-affected cats doing these activities. Then share the results with your veterinarian during your next appointment as a kick-off for partnering in monitoring that your cat’s normal.
ZPC-00435R2
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION: For use in cats only. Women who are pregnant, trying to conceive or breastfeeding should take extreme care to avoid self-injection. Allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, could potentially occur with self-injection. Solensia should not be used in breeding cats or in pregnant or lactating queens. Solensia should not be administered to cats with a known allergy to frunevetmab. The most common adverse events reported in a clinical study were vomiting and injection site pain. Solensia may be associated with scabbing of the head and neck, dermatitis, and pruritus. See full Prescribing Information.
INDICATION: For the control of pain associated with osteoarthritis in cats.
- Lascelles BD, Henry JB 3rd, Brown J et al.: Cross-sectional study of the prevalence of radiographic degenerative joint disease in domesticated cats. Vet Surg 2010; 39: 535&8209;44.


.jpg)

