Arthritis (also known as osteoarthritis, or OA) is an extremely common, painful disease that affects about 40%1 of dogs. It doesn’t matter if the dog is young or old, big or small, purebred or mixed.
Unfortunately, OA is a painful, progressive disease that cannot be cured. But the good news is that pain can be managed with a prescription medication from your veterinarian, and your dog can be made more comfortable. Even better news is that we’re learning more every day about canine OA. So, let’s start with what’s known to-date about osteoarthritis.
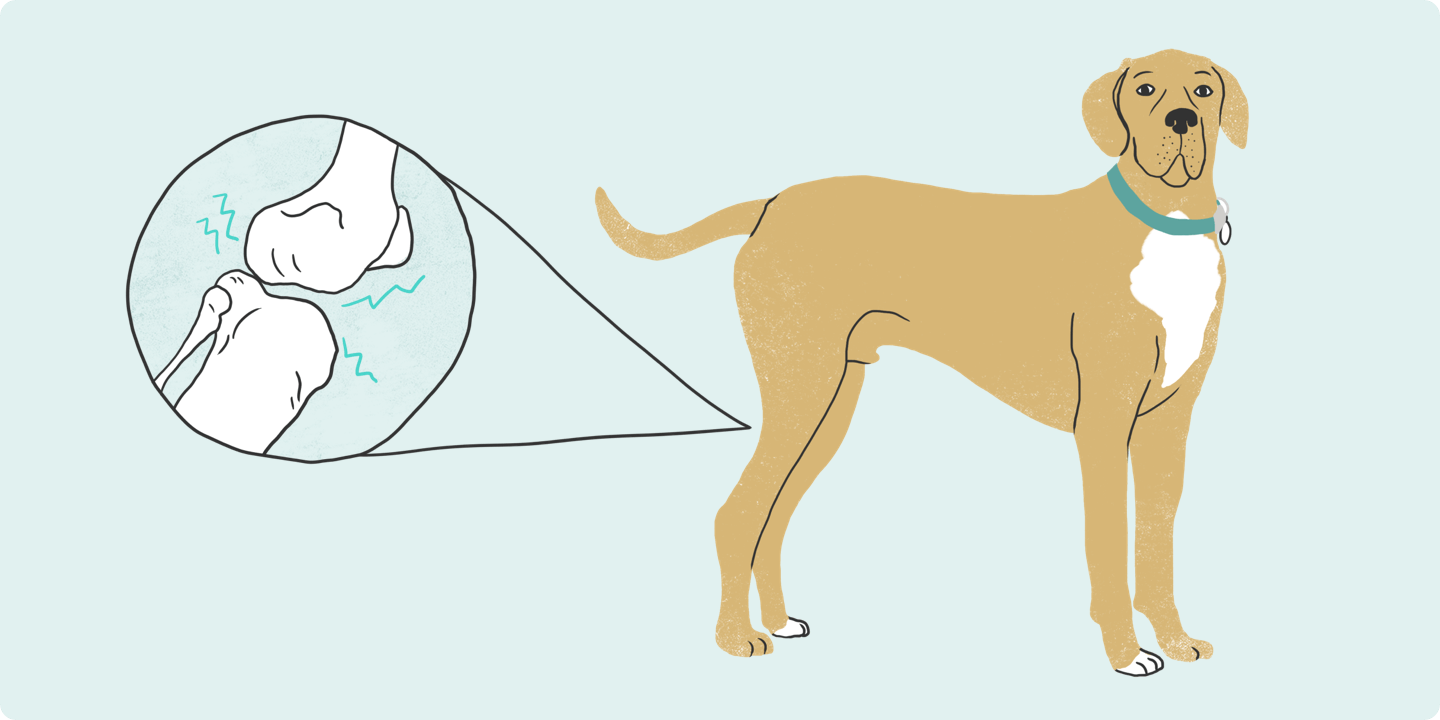
What Is Osteoarthritis?
‘Osteo’ means ‘bone,’ ‘arthra’ means joint, and ‘itis’ means inflammation. Altogether, osteoarthritis is an inflammatory condition of one or more joints. OA is a result of poor joint structure from birth, traumatic injury or normal wear and tear on the joints as the dog ages. Obesity is also a risk factor for OA and contributes to the pain of OA2.
All of these triggers are considered by your veterinarian when they design a treatment plan for your dog.
Pain Management for OA
The pain of OA is progressive: without intervention, it will worsen over time. But there are pain-management medicines made just for dogs. Your veterinarian may prescribe either an anti-NGF monoclonal antibodies or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) to control the pain of OA. It’s important to only use these medicines as prescribed by your veterinarian because some medicines work better together than others and human medicines like aspirin can be toxic to dogs. It's helpful to have questions for your vet about your pet's medication. This is where your veterinarian’s expertise is critical and why it’s important to keep your veterinarian up-to-date with all medicines, supplements, and other treatments that your dog has been given.
Bottom line: Your dog’s pain can be relieved. Remember, your dog’s history is key to determining an effective treatment plan, and you know a lot about your dog.
Share What You Know With Your Veterinarian, Including:
- Has your dog ever been injured?
- Has your dog been slowing down, reluctant to participate in activities they used to enjoy?
- Has your dog gained weight in the past year?
You know your dog best and can provide your vet with crucial insight during your dog’s exam. We recommend filling out our short and simple OA quiz and share it with your veterinarian. What you learn can make a big difference to your dog!
RIM-00253R2
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION: Librela is for use in dogs only. Women who are pregnant, trying to conceive or breastfeeding should take extreme care to avoid self-injection. Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, could potentially occur with self-injection. Librela should not be used in breeding, pregnant, or lactating dogs. Librela should not be administered to dogs with known hypersensitivity to bedinvetmab. Adverse events reported post-approval include ataxia (lack of balance/coordination), anorexia (loss of appetite), lethargy (tiredness), emesis (vomiting), and polydipsia (increased drinking). The most common adverse events reported in a clinical study were urinary tract infections, bacterial skin infections and dermatitis (skin irritation/inflammation). See full Prescribing Information.
See the Client Information Sheet for more information about Librela.
- Wright A., et al. Identification of canine osteoarthritis using an owner-reported questionnaire and treatment monitoring using functional mobility tests. Journal of Small Animal Practice (2022), 1–10 DOI: 10.1111/jsap.13500
- Anderson KL et al. Risk Factors for Canine Osteoarthritis and Its Predisposing Arthropathies: A Systematic Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 7:220. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00220




